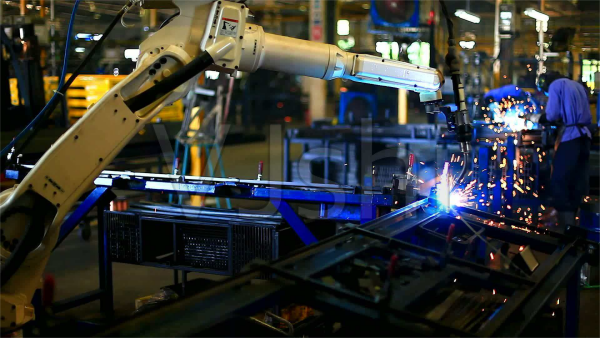
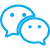
Adopting advanced and applicable new casting technologies, improving the automation of casting equipment, especially the application of industrial robot automation technology, is a key measure for casting enterprises to implement sustainable development.
In casting production, industrial robots can not only replace people working in high temperature, polluted and dangerous environments, but also improve work efficiency, improve product precision and quality, reduce costs, reduce waste, and obtain flexible and long-lasting high-speed production processes. The organic combination of casting equipment and industrial robots has covered various fields such as die casting, gravity casting, low-pressure casting and sand casting, mainly involving core making, casting, cleaning, machining, inspection, surface treatment, transportation and palletizing.
The foundry workshop is particularly prominent, full of high temperature, dust, noise, etc., and the working environment is extremely harsh. Industrial robots can be applied to gravity casting, low-pressure casting, high-pressure casting, spin casting, covering workshops with different casting methods of black and non-ferrous casting, greatly reducing the labor intensity of employees.
According to the characteristics of castings, industrial robot gravity casting automation units have a variety of layout formats.
(1) The circular type is suitable for castings with many specifications, simple casting, and small products. Each gravity machine can cast products of different specifications, and the process rhythm can be diverse. One person can operate two gravity machines. Because of the few restrictions, it is the most commonly used mode at present.
(2) The symmetrical type is suitable for castings with complex product structures, sand cores, and complex casting processes. According to the size of the castings, small castings use small inclined gravity machines. The pouring ports are all within the circular trajectory of the industrial robot, and the industrial robot does not move. For large castings, because the corresponding inclined gravity machines are larger, the industrial robot needs to be equipped with a moving axis for pouring. In this mode, the casting products can be diversified and the process rhythm can be inconsistent.
(3) The disadvantage of the side-by-side circular and symmetrical types is that the logistics of the sand core upper parts and the casting lower parts are single-station and relatively scattered, and the use of gravity machines side by side solves this problem. The number of gravity machines is arranged according to the size of the castings and the process rhythm, and the industrial robot is designed to determine whether it needs to move. Auxiliary grippers can be configured to complete the work of sand core placement and casting unloading, achieving a higher degree of automation.
(4) Circular type The casting speed of this mode is more efficient than the previous modes. The gravity machine rotates on the platform, with pouring stations, cooling stations, unloading stations, etc. Multiple gravity machines operate simultaneously at different stations. The pouring robot continuously takes aluminum liquid for pouring at the pouring station, and the picking robot is unloading synchronously (it can also be done manually, but due to its high efficiency, the work intensity is too high). This mode is only suitable for the simultaneous production of castings with similar products, large batches, and consistent beats.
Compared with gravity casting machines, low-pressure casting machines are more intelligent and automated, and manual labor only needs to do auxiliary work. However, for the highly automated management mode, during the casting process, manual labor can supervise one line by one person and only play the role of patrol inspection. Therefore, the unmanned unit of low-pressure casting is introduced, and industrial robots complete all auxiliary work.
There are two modes of application of unmanned low-pressure casting units:
(1) For castings with multiple product specifications, simple casting, and large batches, one industrial robot can manage two low-pressure casting machines. The industrial robot completes all tasks such as product removal, filter placement, steel numbering, and wing removal, thus realizing unmanned casting. Due to different spatial layouts, industrial robots can be hung upside down or floor-standing.
(2) For castings with single product specifications, requiring manual placement of sand cores, and large batches, industrial robots directly take the parts from the low-pressure machine, cool them, or place them on the drilling machine and transfer them to the subsequent process.
3) For castings that require sand cores, if the sand core structure is simple and the sand core is single, industrial robots can also be used to add the function of taking and placing the sand cores. Manual placement of sand cores requires entering the mold cavity, and the temperature inside the mold is very high. Some sand cores are heavy and require the assistance of multiple people to complete. If the operation time is too long, the mold temperature will drop, affecting the casting quality. Therefore, it is necessary to use industrial robots to replace the sand core placement.
At present, the front-end work of high-pressure casting, such as pouring and spraying molds, has been completed by advanced mechanisms, but the removal of castings and cleaning of the material heads are mostly done manually. Due to factors such as high temperature and weight, the labor efficiency is low, which in turn restricts the production capacity of the casting machine. Industrial robots are not only efficient in taking out parts, but also simultaneously complete the work of cutting the material heads and slag bags, cleaning the flying fins, etc., making full use of industrial robots to maximize the return on investment.
Post time: Jul-08-2024