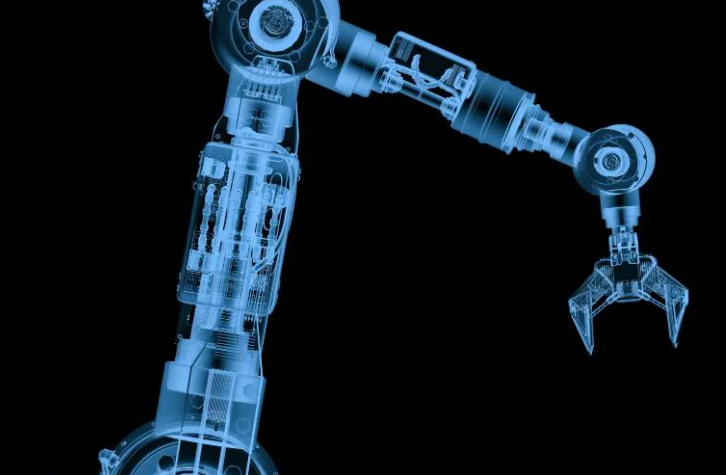
What is an industrial robot?
“Robot” is a keyword with a wide range of meanings that fluctuate greatly. Various objects are associated, such as humanoid machines or large machines that people enter and manipulate.
Robots were first conceived in Karel Chapek’s plays in the early 20th century, and then were depicted in many works, and products named after this name have been released.
In this context, robots today are considered diverse, but industrial robots have been used in many industries to support our lives.
In addition to the automobile and automobile parts industry and the machinery and metal industry, industrial robots are now increasingly used in various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing and logistics.
If we define industrial robots from the perspective of roles, we can say that they are machines that help improve industrial productivity because they mainly engage in heavy work, heavy labor, and work that requires precise repetition, rather than people.
History of Industrial Robots
In the United States, the first commercial industrial robot was born in the early 1960s.
Introduced to Japan, which was in a period of rapid growth in the second half of the 1960s, initiatives to produce and commercialize robots domestically began in the 1970s.
Thereafter, due to the two oil shocks in 1973 and 1979, prices rose and the momentum to reduce production costs strengthened, which would permeate the entire industry.
In 1980, robots began to spread rapidly, and it is said to be the year when robots became popular.
The purpose of early use of robots was to replace demanding operations in manufacturing, but robots also have the advantages of continuous operation and accurate repetitive operations, so they are more widely used today to improve industrial productivity. The application field is expanding not only in manufacturing processes but also in various fields including transportation and logistics.
Configuration of robots
Industrial robots have a mechanism similar to that of the human body in that they carry work rather than people.
For example, when a person moves his/her hand, he/she transmits commands from his/her brain through his/her nerves and moves his/her arm muscles to move his/her arm.
An industrial robot has a mechanism that acts as an arm and its muscles, and a controller that acts as a brain.
Mechanical part
The robot is a mechanical unit. The robot is available in various portable weights and can be used according to the job.
In addition, the robot has multiple joints (called joints), which are connected by links.
Control unit
The robot controller corresponds to the controller.
The robot controller performs calculations according to the stored program and issues instructions to the servo motor based on this to control the robot.
The robot controller is connected to a teaching pendant as an interface for communication with people, and an operation box equipped with start and stop buttons, emergency switches, etc.
The robot is connected to the robot controller via a control cable that transmits power to move the robot and signals from the robot controller.
The robot and robot controller allow the arm with memory movement to move freely according to instructions, but they also connect peripheral devices according to the application to perform specific work.
Depending on the work, there are various robot mounting devices collectively called end effectors (tools), which are mounted on the mounting port called mechanical interface at the tip of the robot.
In addition, by combining the necessary peripheral devices, it becomes a robot for the desired application.
※For example, in arc welding, the welding gun is used as the end effector, and the welding power supply and feeding device are used in combination with the robot as peripheral equipment.
In addition, sensors can be used as recognition units for robots to recognize the surrounding environment. It acts as a person’s eyes (vision) and skin (touch).
The information of the object is obtained and processed through the sensor, and the movement of the robot can be controlled according to the state of the object using this information.
Robot mechanism
When the manipulator of an industrial robot is classified by mechanism, it is roughly divided into four types.
1 Cartesian Robot
The arms are driven by translation joints, which has the advantages of high rigidity and high precision. On the other hand, there is a disadvantage that the operating range of the tool is narrow relative to the ground contact area.
2 Cylindrical Robot
The first arm is driven by a rotary joint. It is easier to ensure the range of motion than a rectangular coordinate robot.
3 Polar Robot
The first and second arms are driven by a rotary joint. The advantage of this method is that it is easier to ensure the range of motion than a cylindrical coordinate robot. However, the calculation of the position becomes more complicated.
4 Articulated Robot
A robot in which all arms are driven by rotation joints has a very large range of motion relative to the ground plane.
Although the complexity of the operation is a disadvantage, the sophistication of electronic components has enabled complex operations to be processed at high speed, becoming the mainstream of industrial robots.
By the way, most industrial robots of the articulated robot type have six rotation axes. This is because the position and posture can be arbitrarily determined by giving six degrees of freedom.
In some cases, it is difficult to maintain the 6-axis position depending on the shape of the workpiece. (For example, when wrapping is required)
To cope with this situation, we have added an additional axis to our 7-axis robot lineup and increased the attitude tolerance.
Post time: Feb-25-2025